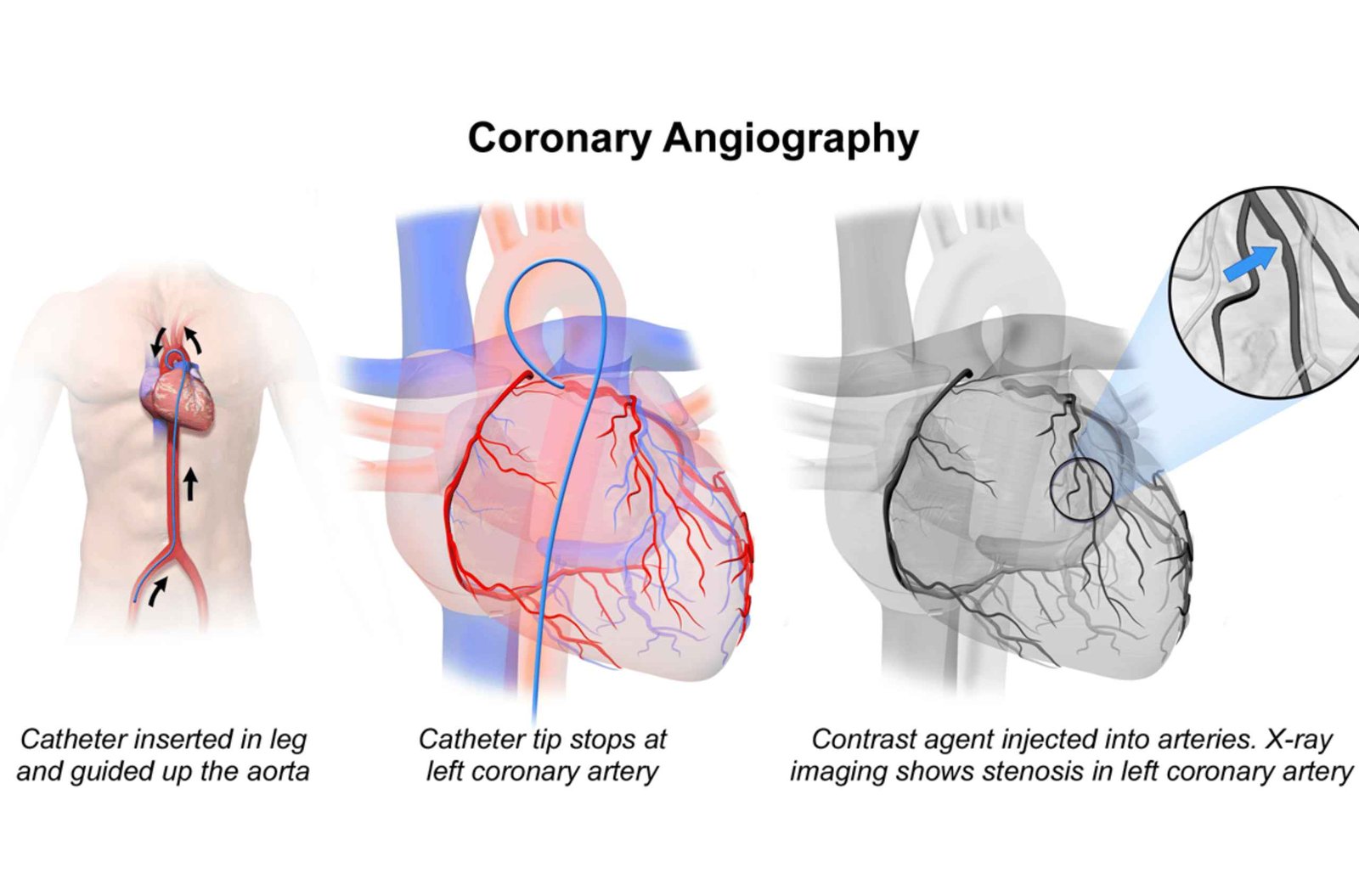
Coronary Angiography is a crucial diagnostic procedure used to visualize the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. This test helps in identifying blockages or narrowing in these arteries, providing essential information for diagnosing and treating heart disease.
Coronary Angiography is a specialized X-ray test that uses a contrast dye and imaging to see the inside of the coronary arteries. The procedure involves threading a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart and injecting a contrast dye that highlights the coronary arteries on X-ray images.
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
Dr. Amit often recommends Coronary Angiography to:
To prepare for the procedure, Dr. Amit advises patients to:
During the Coronary Angiography:
After the procedure:
Consider getting a Coronary Angiography if you:
Coronary Angiography is a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of heart disease. It provides detailed images of the coronary arteries, helping Dr Amit accurately identify blockages and plan effective treatments. With its ability to offer real-time, precise information, Coronary Angiography plays a critical role in ensuring optimal heart health and preventing serious cardiac events.
Coronary Angiography is a diagnostic procedure that uses X-ray imaging to see the heart’s blood vessels. It involves the injection of a contrast dye through a catheter to visualize any blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries.
Dr. Amit may recommend a Coronary Angiography to diagnose coronary artery disease, assess symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath, plan treatment strategies, or evaluate the severity of existing heart conditions.
Preparation includes fasting for several hours before the test, informing Dr. Amit about any medications and allergies, and providing a detailed medical history. Specific instructions regarding medication adjustments will also be given.
During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in your groin or arm and guided to your heart. Contrast dye is injected through the catheter, and X-ray images are taken to visualize the coronary arteries. The procedure typically lasts about 30 minutes to an hour.
The procedure is generally not painful. You may feel a brief sting when the local anesthesia is administered and a warm sensation when the contrast dye is injected. The procedure itself is usually well-tolerated.
While the procedure is generally safe, potential risks include bleeding or bruising at the catheter insertion site, allergic reactions to the contrast dye, arrhythmias, heart attack, stroke, or kidney damage, particularly in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions. Dr. Amit will take precautions to minimize these risks.
Recovery time is usually short. Most patients can go home the same day, but you will need someone to drive you. You should avoid strenuous activities for a day or two and follow Dr. Amit’s instructions regarding care of the insertion site.
Abnormal results indicate the presence of blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries. Depending on the severity, Dr. Amit may recommend further treatments such as angioplasty, stenting, or coronary artery bypass surgery.
Yes, most patients can resume normal activities within a day or two, but it is important to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise until Dr. Amit advises it is safe to do so. Follow specific post-procedure care instructions provided by your healthcare team.